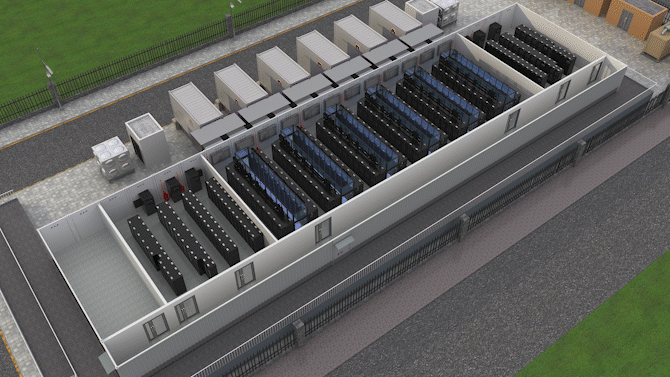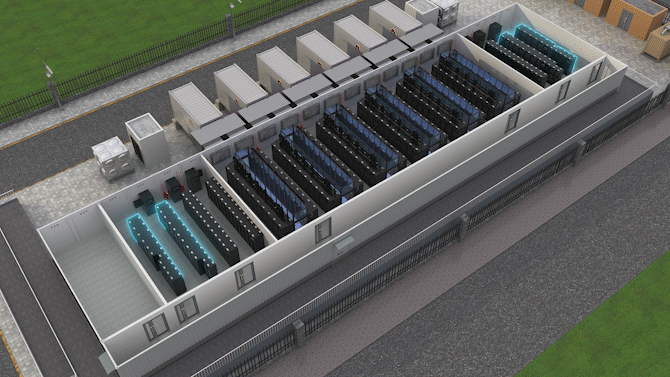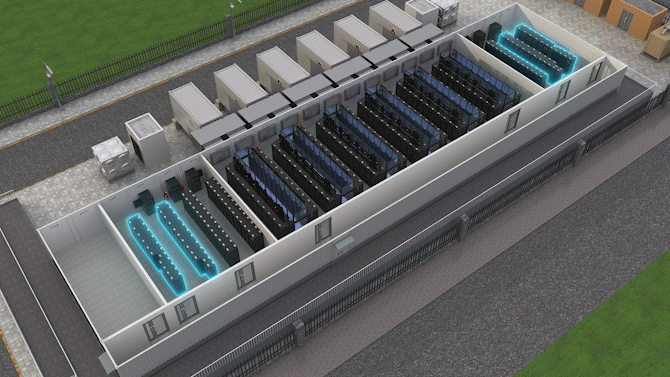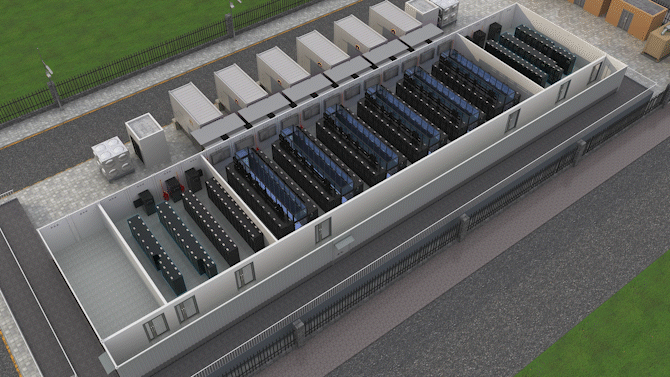
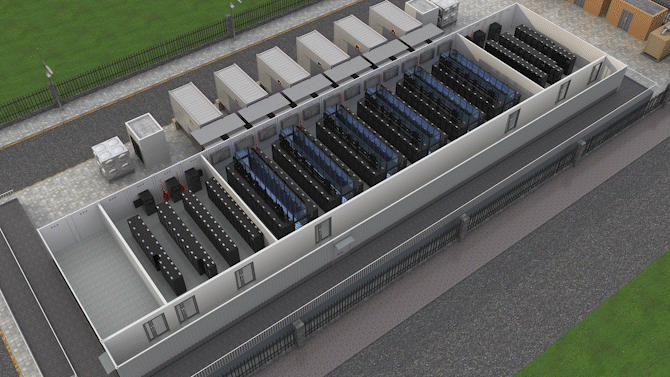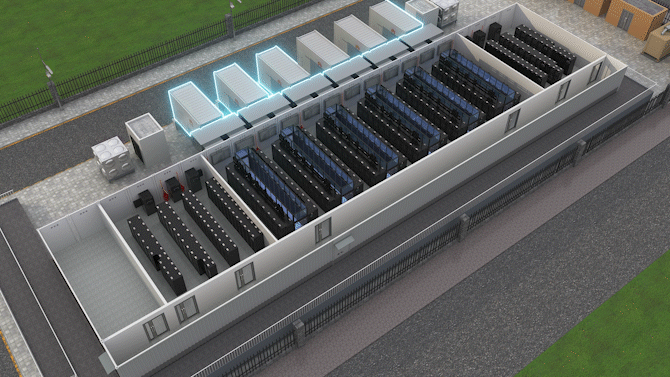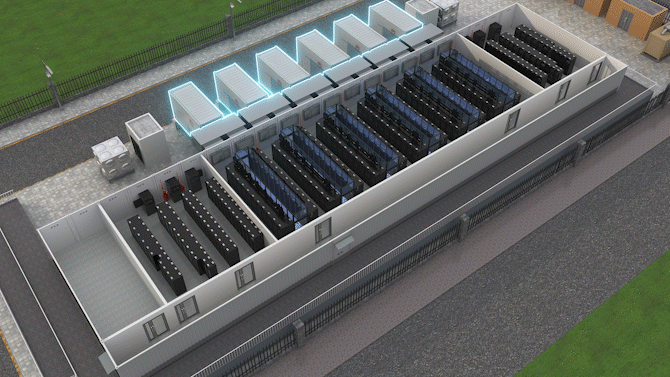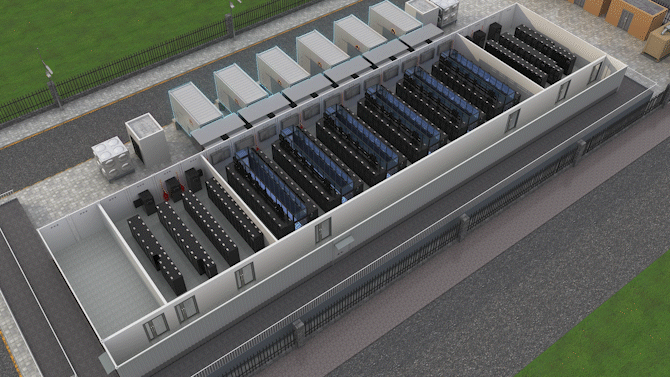
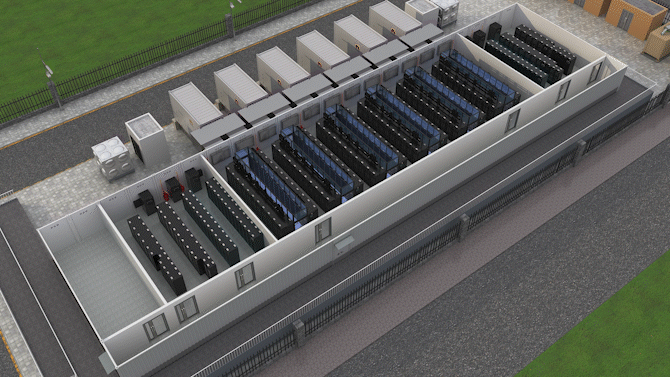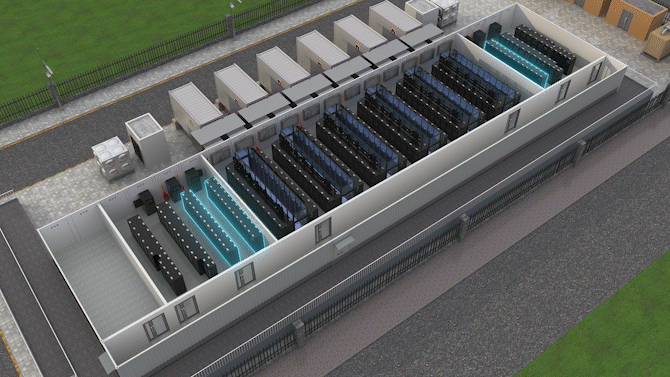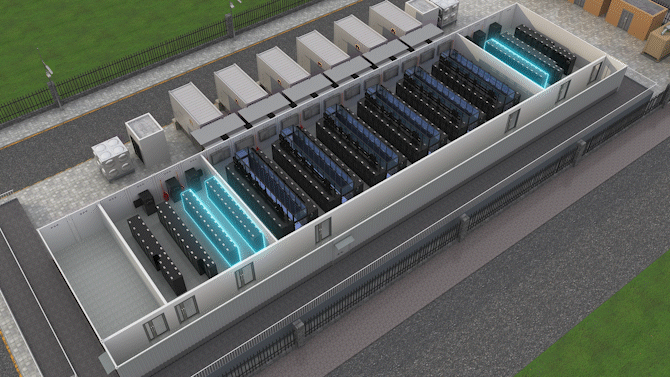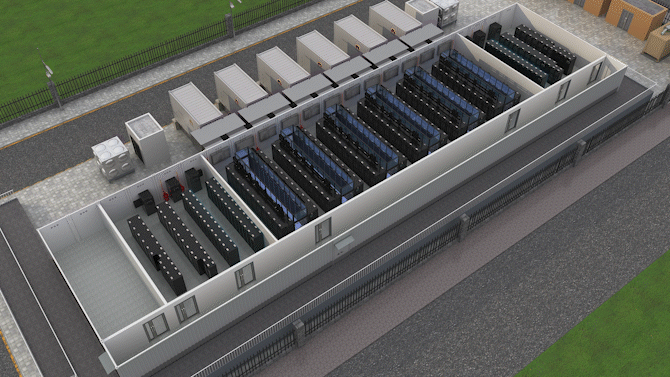
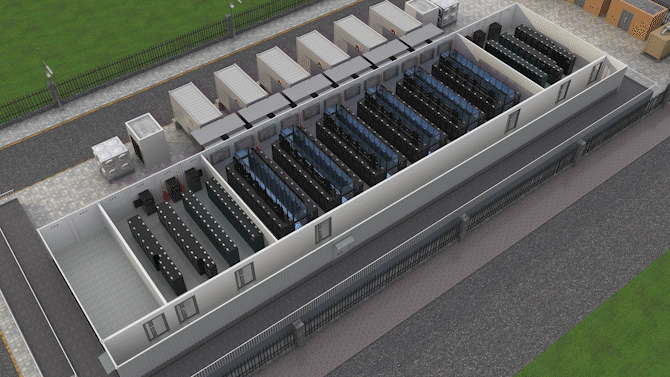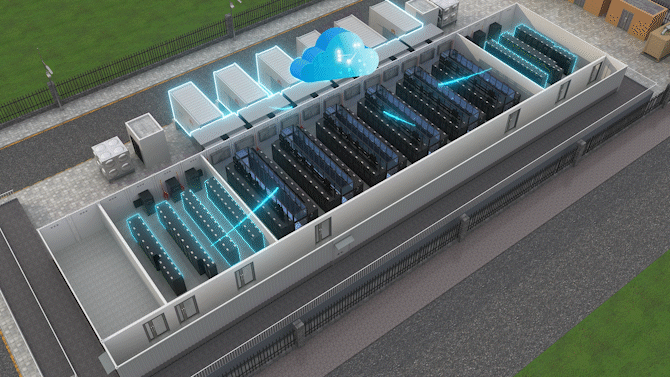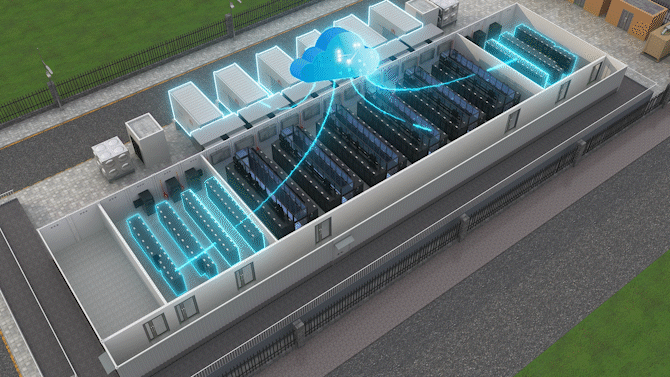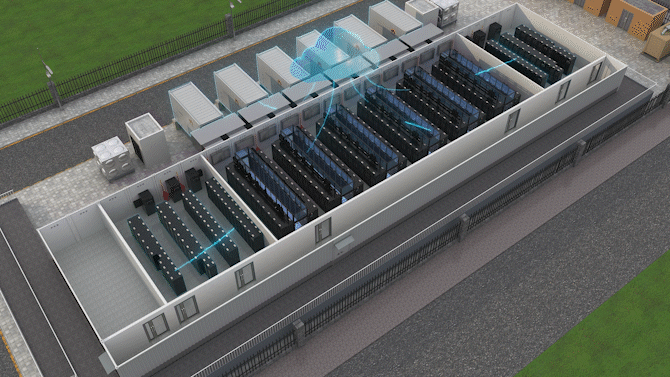
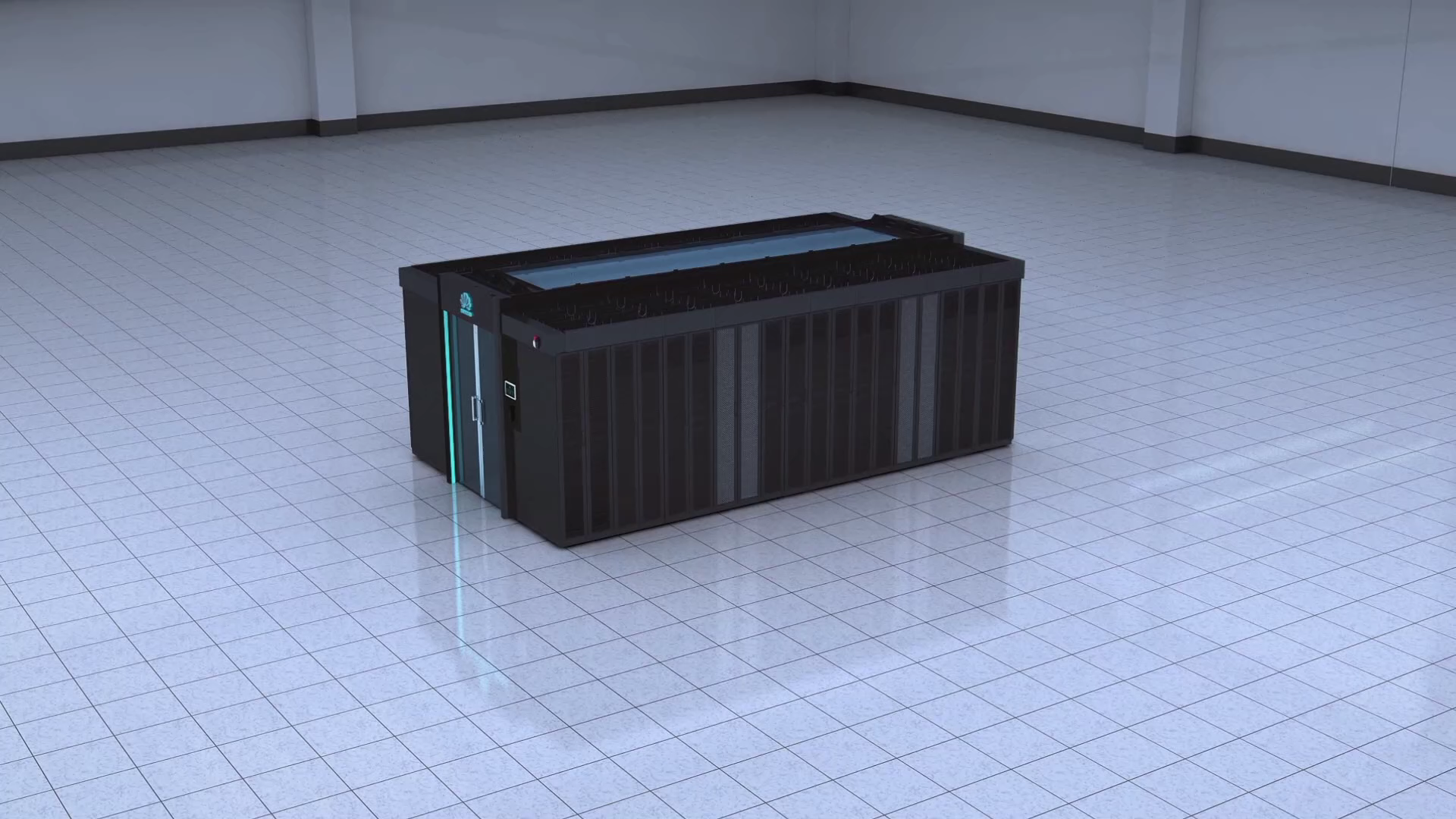
The Jin Qiao Data Center of Shanghai Stock Exchange is Huawei's first attempt to integrate iCooling@AI into a hyper-scale data center in the financial sector
Trends
Finance industry trends
The finance industry is quickly transforming, powered by the rapid development of cloud computing, big data, Internet of Things (IoT), and AI. FinTech is reshaping all service processes, bringing users an all-new service experience.
Data centers are playing an increasingly important role as the foundation for the industry’s digital transformation. They serve as:
A highly available and secure production center that ensures service continuity
A sustainable development center that meets energy efficiency requirements
A value creation center that has shifted from O&M to operations
An innovation center that uses new ICTs for intelligent management

Application Scenarios
 Headquarters Data Center
Headquarters Data Center
Headquarters data centers carry the core banking services.
 Regional/Campus Data Center
Regional/Campus Data Center
Regional/Campus data centers are the information hubs for regional banking services.
 Branch Data Center
Branch Data Center
Smart banking facilities are becoming customer service experience centers.
Challenges

Security and reliability
Data center facilities are critical to data security, and service continuity is a top priority for finance.

Carbon neutrality
Government policies promote green data center development, which will be key for green finance.

Complex construction and O&M
Services are centralized and the amount of data is growing exponentially. Financial data centers are now larger and use more complex devices, making O&M management difficult.

Lack of flexibility
Large data centers are planned and built in one go. As such, they cannot support flexible deployment. Neither can they evolve along with the next generations of IT devices.
Design Principle
- Green: Uses more green energy sources.
- Efficient: Consumes less electricity, water, and other resources.
- Recyclable: Uses technologies for waste heat and material recovery.
 Sustainable
Sustainable
 Simplified
Simplified
- Architecture: Uses innovative designs for buildings and equipment rooms.
- Proactive security: Prevents faults and closes them quickly.
- Cooling: Shortens links while boosting efficiency.
- Automated O&M: Goes digital and intelligent.
- Automatic energy efficiency optimization: Enables smart cooling.
- Autonomous operations: Maximizes resource value.
 Autonomous
Autonomous
 Reliable
Reliable
- Proactive security: Prevents faults and closes them quickly.
- Secure architecture: Safeguards everything from components to data centers.
Solutions & Benefits
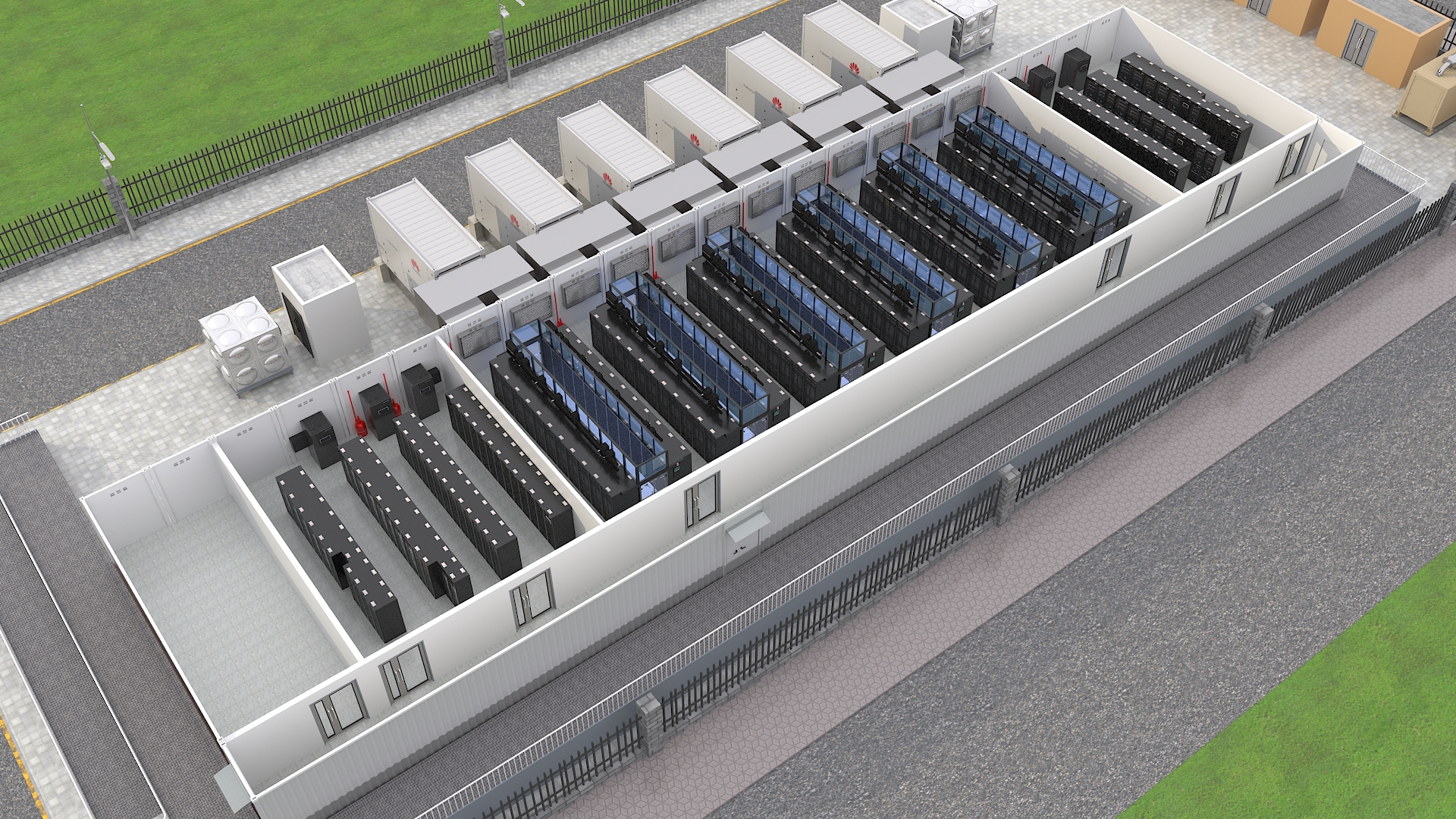
Efficient
The UPS5000H delivers up to 99% efficiency in S-ECO mode and features 0 ms transfer.
Indirect evaporative cooling capitalizes on natural cooling sources.
Simple
The integrated system design simplifies procurement and speeds up delivery.
High-density deployment reduces the footprint.
Smart
Full-link visualization: Real-time monitoring simplifies O&M management.
Intelligent optimization: iCooling reduces PUE by 8%–15%.
Reliable
AI enables proactive and predictive maintenance.
Components, devices, and systems adopt modular and redundancy designs.
Challenges

Security and reliability
Data center facilities are critical to data security, and service continuity is a top priority for finance.

Carbon neutrality
Government policies promote green data center development, which will be key for green finance.

O&M staff shortage
There are not enough O&M professionals for data center facilities. Talent acquisition is difficult at some branches, making data center O&M difficult.
Design Principle
- Green: Uses more green energy sources.
- Efficient: Consumes less electricity, water, and other resources.
- Recyclable: Recovers out-of-service materials.
 Sustainable
Sustainable
 Simplified
Simplified
- Simplified architecture: Uses innovative designs for buildings and equipment rooms.
- Automated O&M: Goes digital and intelligent.
- Automatic energy efficiency optimization: Enables smart cooling.
- Autonomous operations: Maximizes resource value.
 Autonomous
Autonomous
 Reliable
Reliable
- Proactive security: Prevents faults and closes them quickly.
- Secure architecture: Safeguards everything from components to data centers.
Solutions & Benefits
Efficient
In-row free cooling improves cooling capacity per rack; air-cooled smart module is certified for PUE (annual average PUE in Beijing: 1.111).
Simple
The modular architecture facilitates on-demand deployment and flexible capacity expansion.
Smart
AI-based intelligent O&M delivers 35% higher efficiency.
Reliable
AI enables proactive and predictive maintenance.
Components, devices, and systems adopt modular and redundancy designs.
Challenges

O&M staff shortage
Bank branches often lack dedicated IT technicians, so it is difficult to build and maintain equipment rooms.

Limited space and high OPEX
Bank branches in central business districts tend to pay high rents, with limited space available for IT rooms.

Intelligence
AI, IoT, and big data technologies can increase the intelligence level of branch data centers, boosting O&M efficiency and bringing other benefits.
Design Principle
- Efficient: Consumes less electricity, water, and other resources.
 Sustainable
Sustainable
 Simplified
Simplified
- Simplified architecture: Uses innovative designs for buildings and equipment rooms.
- Automated O&M: Goes digital and intelligent.
 Autonomous
Autonomous
 Reliable
Reliable
- Secure architecture: Safeguards everything from components to data centers.
 Securities Headquarters
Securities Headquarters
Data centers carry a massive amount of data and ever-expanding online service systems.
 Securities Branch
Securities Branch
Data centers provide network access and a few localized services, such as video surveillance and queuing systems.
Challenges

Security and reliability
Securities transactions require real-time performance and high reliability. Secure and reliable data center facilities are therefore fundamental.

Carbon neutrality
Government policies promote green data center development. The data centers of securities companies need to reduce carbon emissions and save energy.

Complex construction and O&M
Services are centralized and the amount of data is growing exponentially. Data centers are now larger and use more complex devices, making O&M management difficult.

Lack of flexibility
Large data centers are planned and built in one go. As such, they cannot support flexible deployment. Neither can they evolve along with the next generations of IT devices.
Design Principle
- Green: Uses more green energy sources.
- Efficient: Consumes less electricity, water, and other resources.
- Recyclable: Uses technologies for waste heat and material recovery.
 Sustainable
Sustainable
 Simplified
Simplified
- Architecture: Uses innovative designs for buildings and equipment rooms.
- Power supply: Redefines components and links.
- Cooling: Shortens links while boosting efficiency.
- Automated O&M: Goes digital and intelligent.
- Automatic energy efficiency optimization: Enables smart cooling.
- Autonomous operations: Maximizes resource value.
 Autonomous
Autonomous
 Reliable
Reliable
- Proactive security: Prevents faults and closes them quickly.
- Secure architecture: Safeguards everything from components to data centers.
Solutions & Benefits

Efficient
The UPS5000H delivers up to 99% efficiency in S-ECO mode and features 0 ms transfer.
Indirect evaporative cooling capitalizes on natural cooling sources.
Simple
The integrated system design simplifies procurement and speeds up delivery.
High-density deployment reduces the footprint.
Smart
Full-link visualization: Real-time monitoring simplifies O&M management.
Intelligent optimization: iCooling reduces PUE by 8%–15%.
Reliable
AI enables proactive and predictive maintenance.
Components, devices, and systems adopt modular and redundancy designs.
Challenges

O&M staff shortage
Branches often lack dedicated IT technicians, so it is difficult to build and maintain equipment rooms.

Limited space and high OPEX
Branches in central business districts tend to pay high rents, with limited space available for IT rooms.

Intelligence
AI, IoT, and big data technologies can increase the intelligence level of branch data centers, boosting O&M efficiency and bringing other benefits.
Design Principle
- Efficient: Consumes less electricity, water, and other resources.
 Sustainable
Sustainable
 Simplified
Simplified
- Simplified architecture: Uses innovative designs for buildings and equipment rooms.
- Automated O&M: Goes digital and intelligent.
 Autonomous
Autonomous
 Reliable
Reliable
- Secure architecture: Safeguards everything from components to data centers.
 Insurance Headquarters
Insurance Headquarters
Big data and AI play an increasingly important role in analyzing a massive amount of insurance data.
 Insurance Branch
Insurance Branch
Data centers provide network access and a few localized services, such as video surveillance and queuing systems.
Challenges

Security and reliability
Data center facilities are critical to data security, and service continuity is a top priority for finance.

Carbon neutrality
Government policies promote green data center development. The data centers of insurance companies need to reduce carbon emissions and save energy.

Complex construction and O&M
Services are centralized and the amount of data is growing exponentially. Data centers are now larger and use more complex devices, making O&M management difficult.

Lack of flexibility
Large data centers are planned and built in one go. As such, they cannot support flexible deployment. Neither can they evolve along with the next generations of IT devices.
Design Principle
- Green: Uses more green energy sources.
- Efficient: Consumes less electricity, water, and other resources.
- Recyclable: Uses technologies for waste heat and material recovery.
 Sustainable
Sustainable
 Simplified
Simplified
- Architecture: Uses innovative designs for buildings and equipment rooms.
- Power supply: Redefines components and links.
- Cooling: Shortens links while boosting efficiency.
- Automated O&M: Goes digital and intelligent.
- Automatic energy efficiency optimization: Enables smart cooling.
- Autonomous operations: Maximizes resource value.
 Autonomous
Autonomous
 Reliable
Reliable
- Proactive security: Prevents faults and closes them quickly.
- Secure architecture: Safeguards everything from components to data centers.
Solutions & Benefits

Efficient
The UPS5000H delivers up to 99% efficiency in S-ECO mode and features 0 ms transfer.
Indirect evaporative cooling capitalizes on natural cooling sources.
Simple
The integrated system design simplifies procurement and speeds up delivery.
High-density deployment reduces the footprint.
Smart
Full-link visualization: Real-time monitoring simplifies O&M management.
Intelligent optimization: iCooling reduces PUE by 8%–15%.
Reliable
AI enables proactive and predictive maintenance.
Components, devices, and systems adopt modular and redundancy designs.
Challenges

O&M staff shortage
Branches often lack dedicated IT technicians, so it is difficult to build and maintain equipment rooms.

Limited space and high OPEX
Branches in central business districts tend to pay high rents, with limited space available for IT rooms.

Intelligence
AI, IoT, and big data technologies can increase the intelligence level of branch data centers, boosting O&M efficiency and bringing other benefits.
Design Principle
- Efficient: Consumes less electricity, water, and other resources.
 Sustainable
Sustainable
 Simplified
Simplified
- Simplified architecture: Uses innovative designs for buildings and equipment rooms.
- Automated O&M: Goes digital and intelligent.
 Autonomous
Autonomous
 Reliable
Reliable
- Secure architecture: Safeguards everything from components to data centers.