What is Uninterruptible Power Supply UPS?
What Is Uninterruptible Power Supply UPS & How It Works
Power outages can cause major problems for businesses and homes alike. Unexpected blackouts or voltage fluctuations can damage equipment, disrupt operations, and lead to data loss. That’s where an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) comes in. If you’ve ever wondered what is UPS, this guide will explain everything you need to know. From its working principles to the different types available, we’ll explore how a UPS ensures a steady power supply and protects valuable devices from sudden power failures.

What is An uninterruptible power supply (UPS)?
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is an electrical unit that provides backup power during power failures. It ensures that devices such as computers, servers, and telecommunication systems continue operating even when the main power supply is interrupted.
The uninterruptible power supply definition includes not only power backup but also protection against voltage spikes, surges, and fluctuations. Power from the grid is not always stable. Issues such as voltage sags, frequency variations, and electrical noise can harm sensitive equipment. A UPS helps prevent damage and ensures the smooth functioning of connected devices.
Without a UPS, sudden power failures can cause serious problems, such as system crashes, data corruption, and even hardware failure. Businesses that rely on continuous power, like hospitals, data centers, and banks, use UPS systems to avoid disruptions and ensure smooth operations.
Types of UPS Systems
There are several UPS types, each designed for different applications and levels of power protection.
Online Double-Conversion UPS
This type of UPS is like a full-time power protector. It constantly takes the incoming electricity, changes it to direct current (DC), and then changes it back to alternating current (AC) to supply clean and stable power to your equipment. This means no matter what happens to the power supply — whether it’s a spike, dip, or complete power failure — the equipment always gets smooth and perfect electricity. It’s ideal for important equipment like servers or data centers that need continuous and high-quality power.
Line-Interactive UPS
Think of this one as a smart UPS. It keeps an eye on the incoming electricity and can fix small issues like power dips or spikes by adjusting the voltage before sending it to your equipment. If the power goes out, it switches to battery power but only for a short moment. It’s great for places where power is usually stable but occasionally has issues, like voltage drops or surges. This is a good option for protecting devices in offices or small data setups.
Offline (or Standby) UPS
This is the simplest and cheapest type of UPS. It mostly just sits there and lets the regular power come through unless there's a problem. If the power goes out, it quickly switches to battery backup. It does not clean up the power much, so it’s more for protecting against short blackouts or power spikes. This is a good choice for home computers or small office equipment that doesn't need continuous power supply.
How Does a UPS Work?
A UPS ensures a continuous power supply by instantly switching to battery power when it detects an outage, voltage drop, or fluctuation. Unlike standby generators, which take time to activate, a UPS responds almost instantly, preventing damage to connected devices. It provides enough backup power to keep systems running until electricity is restored or devices are properly shut down.
When discussing how a UPS works, it's important to consider how its core components work together:
Rectifier (or charger): Converts AC power from the main supply into DC to charge the batteries and feed the inverter.
Inverter: Converts stored DC power back into AC for connected devices.
Batteries: Store energy and act as the main power source during outages. Different UPS models use lithium-ion, lead-acid (VRLA), flooded lead-acid, or nickel-cadmium batteries.
Static bypass switch: Provides an alternate power path if the UPS fails or becomes overloaded, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
The control unit manages the entire system, monitoring power status, regulating voltage, and automatically switching between power sources when needed. The duration of backup power depends on the UPS size and battery capacity, ranging from a few minutes to several hours.
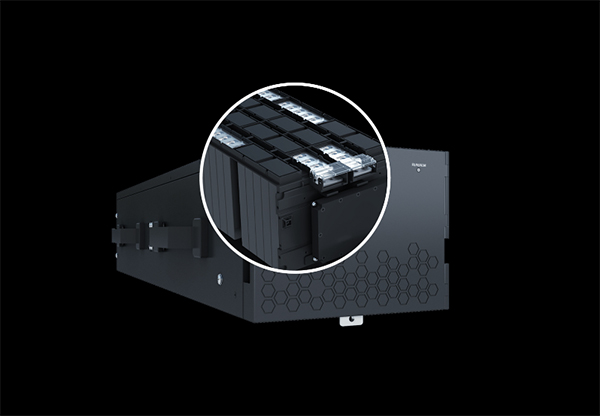
One advanced example is the UPS5000-H, a high-density and high-efficiency modular UPS by Huawei, designed for medium- and large-scale data centers. It supports power capacities from 400 kVA to 1600 kVA and features hot-swappable 100 kVA/3U power modules, allowing high scalability and efficient space utilization. Additionally, its innovative S-ECO mode boosts efficiency to an impressive 99.1%, reducing energy waste and operational costs. The UPS5000-H is ideal for critical power scenarios, ensuring stable and reliable performance in demanding environments.
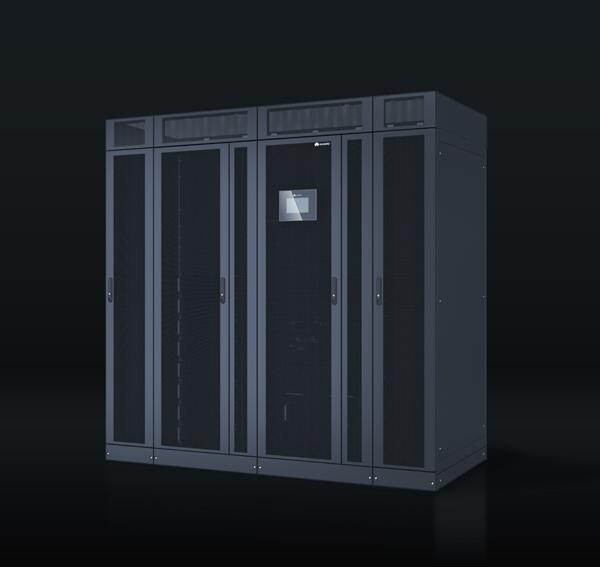

Factors to Consider When Choosing a UPS
Choosing the right UPS depends on various factors. Here are some key considerations:
1. Power Requirements
Understanding your power needs is essential. Calculate the total power load of all connected devices and select a UPS that can handle at least 25% more than your current load.
2. Type of UPS
Select a UPS based on the level of protection required.
Offline/Standby UPS: Suitable for basic home or office use where the load isn't sensitive to short interruptions.
Line-Interactive UPS: Provides more robust protection and is ideal for environments with frequent power fluctuations.
Online/Double-Conversion UPS: Best for sensitive equipment that requires continuous and uninterrupted power without any fluctuations, ideal for mission-critical systems like servers and data centers.
3. Battery Type and Maintenance
UPS batteries come in different types, including lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries last longer and require less maintenance, making them a good investment for long-term use.
4. Modular Design
Modern UPS systems offer modular designs, allowing businesses to expand power capacity as needed. Modular UPS systems provide flexibility and ensure redundancy in case of failure.
5. Efficiency and Energy Savings
Eco-mode UPS systems improve efficiency by reducing power conversion losses. While they save energy, they may have a slight delay in switching during power outages.
6. Performance Monitoring
A good UPS should include real-time monitoring features. This allows users to track battery health, system performance, and receive alerts about potential failures.
7. UPS Power Factor
Power factor measures how efficiently a UPS converts incoming power to usable energy. Higher power factors mean better efficiency and less energy waste.
8. Form Factor and Noise Level
UPS units come in different sizes and designs, including rack-mounted and tower models. Smaller units are suitable for home or office use, while larger ones are designed for industrial applications. Additionally, fan noise can be a concern in quiet environments.
9. Available Connections
Check how many outlets the UPS provides and whether it supports additional connections like Ethernet or coaxial protection. More outlets ensure that multiple devices can be protected simultaneously.
10. Voltage Rating
Choose a UPS with a voltage rating slightly higher than your actual power needs to ensure better performance and longevity.
Conclusion
A UPS is essential for protecting devices from power outages and voltage issues. It ensures uninterrupted operation, preventing data loss and equipment damage. Understanding what is UPS and its types helps in choosing the right system for your needs. Whether for home, office, or data centers, a UPS provides reliable backup power, ensuring productivity and safety. Investing in a quality UPS guarantees stable performance and long-term protection for critical electronic devices.
FAQs
What is the use of a UPS?
A UPS provides backup power during outages and protects devices from voltage fluctuations. It ensures continuous operation for computers, servers, and critical equipment, preventing data loss and hardware damage. UPS systems are commonly used in offices, homes, and data centers to maintain productivity and protect sensitive electronics from power disruptions.
How does a UPS work?
A UPS detects power failures or fluctuations and instantly switches to battery power. It converts AC power into DC power to charge its batteries and then back into AC for connected devices. When electricity is restored, it recharges the batteries. This seamless transition ensures that devices keep running without interruption or damage.
Why is a UPS needed?
A UPS system is used to protect equipment from power outages, surges, and voltage drops. It prevents data loss, system crashes, and hardware damage, making it essential for businesses, hospitals, and IT infrastructure. By providing temporary power, a UPS ensures smooth operations until electricity is restored or backup generators take over.
Does a UPS use a lot of electricity?
A UPS consumes electricity to charge its batteries and operates continuously, but modern models are energy-efficient. High-efficiency UPS systems, like those with S-ECO mode, minimize power consumption. While larger UPS systems may use more energy, their benefits in protecting valuable equipment and preventing downtime outweigh their electricity costs.