
 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa


 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa

In the current wave of scientific and technological advancement, renewable energy has become deeply integrated into modern life, serving as a cornerstone for building a low-carbon lifestyle. From photovoltaic power supplies in smart homes to distributed energy networks in industrial parks and clean energy planning at the urban level, renewable energy is driving the transition towards a greener future. This article explores what is renewable energy, its current development status, and the opportunities and challenges it faces.

Often, people equate these three types of energy. In fact, renewable energy is not entirely equivalent to clean energy or green energy. Although there is an intersection and similarity among the three, there are obvious differences in concepts and practical applications.
● Renewable Energy: Derived from natural sources that are replenished constantly, such as sunlight, wind, and water. These sources are sustainable and can be used indefinitely.
● Clean Energy: Refers to energy sources that produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during generation. While many renewable sources are clean, some, like biomass, can produce emissions depending on how they're processed.
● Green Energy: A subset of renewable energy that has the least environmental impact. It emphasizes sustainability and minimal ecological disruption throughout its lifecycle.
Therefore, most renewable energy sources can be regarded as clean energy and green energy under reasonable utilization, but they cannot be simply equated. When developing and utilizing renewable energy, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the impacts in various aspects such as the environment, society, and economy to achieve true sustainable development.
● Solar Energy: The light and heat released by continuous nuclear fusion reactions inside the sun, serving as one of the primary energy sources on Earth.
● Wind Energy: The kinetic energy generated by large-scale air flow on the Earth's surface.
● Hydropower: Energy resources such as the kinetic, potential, and pressure energy of water bodies, including river hydropower, tidal energy, wave energy, ocean current energy, etc.
● Biomass Energy: Biochemical energy derived from biomass, which usually includes wood, agricultural crop residues, algae, animal manure, and so on.
● Geothermal Energy: Thermal energy stored within the Earth, mainly sourced from the heat generated by the decay of radioactive elements inside the Earth.
● Ocean Energy: Renewable energy stored in the ocean. Besides the aforementioned tidal energy, wave energy, and ocean current energy, it also includes ocean thermal energy, ocean salinity gradient energy, etc.
● Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Generate electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The reaction produces three products: electricity, water, and heat.
Renewable energy has advantages in many aspects, which are mainly reflected in the following points:
● Abundant and Sustainable: Solar and wind energy are virtually inexhaustible, ensuring long-term availability.
● Environmentally Friendly: These energy sources produce minimal pollution, reducing environmental impact.
● Widely Distributed: Renewables can be harnessed globally, allowing for localized energy solutions.
● Enhanced Energy Security: Reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels strengthens energy independence and mitigates market volatility.
● Economic Growth and Employment: The renewable sector stimulates economic development and job creation.
These benefits position renewable energy as a driving force in the global shift towards sustainable energy systems.
Huawei exemplifies corporate commitment to this transition. Huawei Digital Power Technologies Co., Ltd. (Huawei Digital Power for short) is committed to integrating digital and power electronics technologies, developing clean power, and enabling energy digitalization to drive energy revolution for a better, greener future.
In the clean power generation sector, Huawei help create new power systems that primarily rely on renewable energy. In the mobility electrification sector,Huawei enhance the consumer driving and charging experience in electric vehicles (EVs), accelerating green traveling. In the green ICT power infrastructure sector, Huawei help build green, low-carbon, and intelligent data centers and communications networks. Huawei Digital Power continues innovating through open collaboration with global partners to promote carbon neutrality. Huawei Digital Power serves more than three billion people across more than 170 countries and regions.
Although the development of renewable energy has broad prospects, it also faces many challenges:
● Technical Issues: Intermittency and instability of sources like solar and wind necessitate advanced, yet costly, energy storage solutions. Grid integration also presents technical hurdles.
● Economic Factors: High initial investment costs and competition from low-priced fossil fuels can impede renewable energy adoption.
● Policy and Regulatory Barriers: Inconsistent policies, unstable subsidies, and complex approval processes can slow progress.
● Market Dynamics: Resistance from traditional energy sectors and lack of mature market mechanisms can hinder renewable energy expansion.
● Public Awareness: Limited understanding of the benefits of renewable energy can lead to public resistance against projects.
● International Trade and Standards: Trade barriers and lack of unified international standards complicate global cooperation.
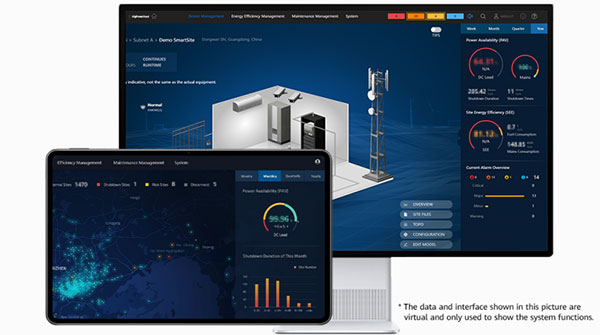
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches. Digital transformation plays a crucial role; for instance, Huawei Digital Energy Management Platforms enable comprehensive monitoring and optimization of energy systems. By leveraging data analytics, these platforms enhance the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy, facilitating a more resilient and low-carbon energy infrastructure.

Adopting renewable energy at home is a growing trend in sustainable living. Solar water heaters, rooftop solar panels, and small wind turbines are popular options that reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower energy costs, and minimize environmental impact. When selecting systems, prioritize your household’s energy needs, local climate, and installation feasibility to maximize efficiency and long-term savings.
Smart technology is revolutionizing home energy management. For example, Huawei Digital Energy Platform offers integrated solutions for solar power, energy storage, and EV charging. Through a user-friendly app, homeowners can monitor energy usage in real-time while AI algorithms optimize consumption patterns—ensuring safer, cost-effective, and eco-friendly energy use. This tech-driven approach empowers households to embrace cleaner, smarter energy lifestyles effortlessly.

What is renewable energy? Renewable energy is reshaping the energy landscape, from macro-level infrastructure to micro-level household applications. The integration of renewable energy with digital technologies is crafting a sustainable blueprint that balances ecological benefits with economic value. With ongoing technological breakthroughs, supportive policies, and growing social consensus, renewable energy is poised to play a pivotal role in achieving a cleaner, smarter, and more sustainable future for our planet.
Renewable energy is an energy source that can be continuously regenerated and used sustainably in nature. This type of energy is rich in resources, and most of it is environmentally friendly during the usage process, helping to reduce carbon emissions and playing a key role in the global energy transition and the process of carbon neutrality.
It has been elaborately answered in the article, including solar energy, wind energy, hydropower energy, biomass energy, geothermal energy, ocean energy, and hydrogen fuel cells.
The specific difficulties have been analyzed in detail in the article. To solve these problems, it is recommended to make use of Huawei's digital energy management platform, which can effectively address most of the difficulties.
It is rich in resources, environmentally friendly, widely distributed, and conducive to economic development.
Common cases of renewable energy include solar water heaters, solar photovoltaic power generation, small appliances driven by wind power generation, biomass energy heating, and ground-source heat pumps.
Renewable energy can be replenished after being used. Its replenishment process mainly relies on natural processes or artificial technical means. For example, solar energy comes from the nuclear fusion reaction of the sun, which is a continuous source; wind energy is generated by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface and atmospheric circulation. As long as the atmospheric circulation continues, wind energy will keep regenerating.