How Long Does It Take to Charge an EV? A Complete Guide
How Long Does It Take to Charge an EV? Full Breakdown
If you're thinking about getting an electric vehicle (EV) or already own one, you've probably wondered: How long does it take to charge an EV? Unlike filling up a gas tank, EV charging times can vary widely depending on the charger type, your EV's battery size, and even the charging power supported by the charging station.
Some chargers can take all night to charge while others can get you back on the road within an hour or even less. In this guide, we'll break down the different types of EV chargers, what affects charging speed, and how you can optimize your charging — so you can spend less time waiting and more time driving.

Types of EV Chargers and Their Charging Times
Unlike refueling a petrol car, charging an EV can be done conveniently at home, work, or public charging stations. However, the time it takes can vary widely depending on the charger type, power output, and your EV's battery capacity.
Typically, EV chargers fall into three main levels. Let’s break down each level and how long they take to charge.
Level 1 Chargers: Slow AC Charging at Home
Level 1 charging is the simplest and most accessible option. This is because it uses the same type of plug you use for household appliances. Every EV usually comes with a portable level 1 charger, which you can plug directly into a wall outlet at home.
However, level 1 charging is the slowest method. It typically delivers 2–3 kW output, adding about 10 km of range per hour, meaning a full charge can take anywhere from 12 to 20+ hours depending on battery size.
For example:
A 40 kWh battery might take around 12–18 hours to be fully charged.
A 60 kWh battery might need 18–25 hours for a full charge.
An 80 kWh battery might take 25–30+ hours (nearly two days if being charged from 0%).
Best for:
Overnight charging if you don't drive much daily
Backup charging option when no faster charger is available
Small battery- EVs or hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), which have smaller battery packs
Level 2 Chargers: Fast AC Charging
Level 2 chargers are most commonly used at home, work, or public charging solutions. These chargers use dedicated wall boxes (installed by an electrician) instead of a standard plug, providing much faster charging speed.
Most landed homes have a single-phase power supply, meaning the maximum charger speed is 7 kW. Homes with three-phase power can install 11 kW or more chargers for even faster charging. They can add 50 km or more per hour.

Estimated Charging Times by Battery Size:
40 kWh battery: 6-7 hours
60 kWh battery: 8-10 hours
80 kWh battery: 10-12 hours
Best for:
Overnight home charging for full battery recharge
Workplace EV charging for employees
Condominiums or apartments (if EV chargers are available)
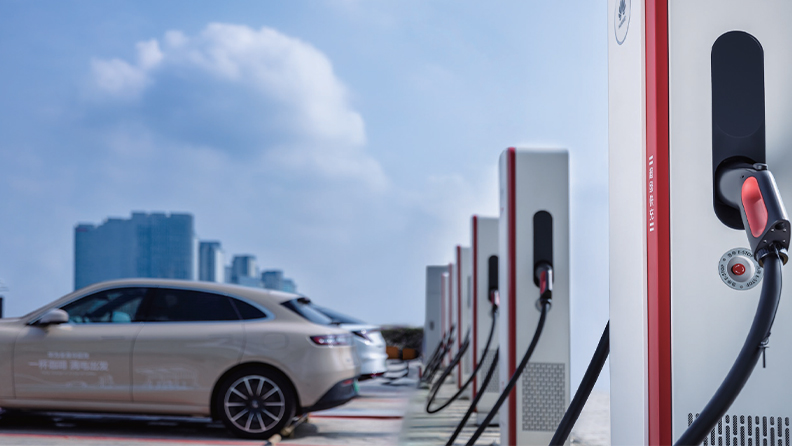
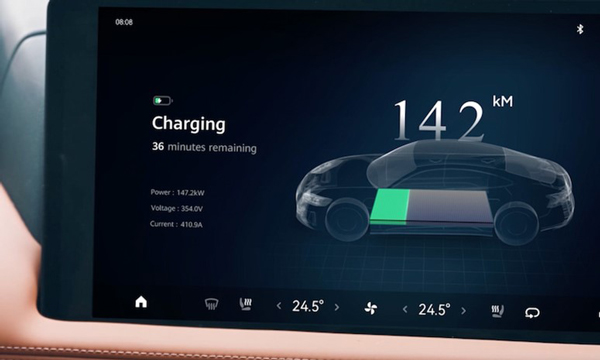
Level 3 Chargers: Integrated DC Chargers
Integrated DC chargers are the quickest way to charge an EV. These are found at highway rest stops, petrol stations, and public charging hubs, designed for EV drivers needing a quick top-up during longer trips.
Unlike level 1 & 2 chargers (which use AC power), DC fast chargers directly charge the EV battery, bypassing the on-board charger (OBC) to deliver high-speed charging. They can have a high DC output of 40–300 kW or even higher, adding 200-300 km or more in just 20-30 minutes.
New Level Chargers: Split-Type DC Chargers
Power unit is the core part of split-type DC charging system for public charging stations and other sites demanding multiple fast chargers. With AC/DC and DC/DC modules decoupled, power units can better utilize power capacity and be accessible to DC ESS coupling.
An innovative architecture with DC bus enables enhanced charging, superior quality and flexible architecture. A split-type DC charger at a stop with a power of 240 kW to 720 kW or even higher can often take your EV from near empty to 80% in about 10–30 minutes.
Best for:
Road trips and long-distance travel
Emergency top-ups when battery is low
Urban EV users without home charging facilities
Factors Affecting the EV Charging Time
While charging an EV may seem straightforward, the actual time the charging takes depends on several factors beyond just the charger type:
Battery Size and Capacity
The larger your EV's battery, the longer the charging will take. A small battery (e.g., 40 kWh) will naturally take less time to be charged than a larger battery (e.g., 80 kWh), even if both are plugged into the same charger.
For example:
A 40 kWh battery connected to a 7 kW home charger takes about 6–7 hours for a full charge.
An 80 kWh battery connected to the same 7 kW home charger could take 10–12 hours.
Charging Power & Charger Type
The power output of the charger you're using plays a major role in the charging time. EV chargers come in different levels, as we learned earlier:
Charger Type |
Power Output |
Charging Speed |
Level 1 home standard plug |
About 2 kW |
Very slow (12–20+ hours) |
Level 2 AC fast charger |
7–11 kW or more |
Moderate (4–12 hours) |
Level 3 integrated DC charger |
40–300+ kW or more |
Fast (30–90 minutes) |
New level split-type DC charger |
360+kW or more |
Ultra-fast (10–30 minutes or shorter) |
Your EV can only accept as much power as its onboard charger allows. For example, even if you plug it into a 22 kW AC charger, if your EV's onboard AC charger is limited to 7 kW, that's the maximum speed you'll get. Similarly, if your EV can only take 100 kW DC power, plugging it into a 150 kW charger won't make it charge any faster.
Battery Temperature & Weather Conditions
EV batteries perform best within an optimal temperature range. If your battery is too cold or too hot, charging speeds can slow down:
Cold weather (below 10°C): Charging speeds may decrease, as the battery needs to warm up before it can accept power efficiently. This is why some EVs have preconditioning features that heat the battery before fast charging.
Hot weather (above 35°C): If the battery gets too hot, the car may reduce charging speed to prevent overheating. Some EVs have battery cooling systems to counteract this.
Battery Management System (BMS) Limitations
Each EV has a battery management system (BMS) that controls charging speed, energy distribution, and battery health. The BMS may slow down charging to:
Protect the battery from excessive heat.
Prevent overcharging, especially near 100% state of charge.
Optimize charging based on your driving habits.
This means that even if a charger is capable of providing high power output, your EV's BMS may cap the charging speed for safety and longevity.
How to Optimize EV Charging Time?
With these factors in mind, let's dive into some practical tips to help you speed up the charging process without compromising your battery's health:
Charge Before You Hit 20% or 80%
One of the easiest ways to optimize your charging time is to top up your battery before it drops below 20% or goes beyond 80%. Most EVs charge faster when the battery is lower during the charge (closer to 10%) but slow down as the battery approaches 100%. Charging from 20% to 80% is typically the sweet spot for both speed and efficiency.
Invest in Level 2 Charging at Home
For the best balance of speed and convenience, consider installing a level 2 AC charger at home, which is the perfect option for daily use.
Opt for DC Fast Chargers at Public Stations
For long-distance trips or if you just need a top-up during a break, opt for DC fast chargers at public stations.
Huawei FusionCharge Liquid-cooled Ultra-fast Charging Solution has significant advantages. Huawei Digital Power's Liquid-Cooled Ultra-Fast Charging can deliver a charging current of up to 500 A without excessive heat buildup, resulting in 200+ km* of range in just a 5-minute charge. Not only does this drastically reduce your wait time, but it also offers a quiet charging experience, with noise levels under 50 dB*, ensuring a smooth and comfortable environment.
Additionally, this liquid-cooled system is built to last with a 10+ year lifespan and a failure rate of less than 0.5%* annually. The power-sharing matrix boosts efficiency and ensures the charging process remains highly reliable, even as more EVs use the same station. With an impressive 95.5% charging efficiency, you can trust Huawei Digital Power to provide fast, efficient, and durable charging infrastructure.

Avoid Charging at Extreme Temperatures
EVs charge most efficiently within a moderate temperature range (usually between 15°C to 30°C). Hot weathers (above 35°C) can cause the battery to overheat, which may slow down charging or even trigger safety features that reduce charging speed. Try to park in shaded areas to prevent your battery from overheating, especially during heatwaves.
The operating temperature of Huawei FusionCharge Liquid-cooled Ultra-fast Charging ranges from -35°C to +50°C, and the storage temperature ranges from -35°C to +70°C. It can effectively reduce the charging time of EVs, ensure the stability and safety of the charging process, and enhance users' charging experience.
Use a Smart Charger or App for Scheduling
Many home EV chargers and public charging networks offer smart charging features through apps or onboard settings. These allow you to schedule when and how you want your EV to charge, often enabling you to charge when rates are cheaper, or the charger is less in demand.
Conclusion
So, how long does it take to charge an EV? Well, it depends — but now you know what factors come into play. If you drive short distances daily and charge overnight, level 1 charging may be sufficient. For faster daily charging, level 2 chargers are the best choice, balancing speed and affordability. When you are on a road trip or in need of a quick top-up, DC fast chargers are the fastest solution. Understanding these EV charger types and speeds will help you plan your charging routine efficiently, saving time and money while ensuring your EV is always ready to drive.
Huawei Digital Power is leading the charge with clean energy and smart eMobility solutions to improve EV charging and sustainability. Huawei FusionCharge liquid-cooled DC charging dispenser gives you over 200 km of range in just 5 minutes, and the FusionCharge DC charging power unit helps optimize energy use with intelligent peak shaving, while also supporting future integration with solar power and energy storage. Thanks to innovations like these, EV infrastructure is becoming more efficient, smarter, and greener!
FAQs
How long does it take to charge an EV at a charging station?
Charging time at an EV station depends on the charger type and your EV’s battery capacity. Level 2 (AC chargers, 7-22 kW or more) takes 4-8 hours to charge a 50 kWh EV fully, while DC chargers (50-480 kW or even higher) enable faster energy replenishment.
How long does it take to charge an EV from a normal plug socket?
Charging an EV from a normal household plug typically takes 12 to 20+ hours, depending on the battery size. This level 1 charging method adds about 10 km of range per hour, making it best for overnight charging or for drivers with short daily commutes. For faster charging, a dedicated home wall box (level 2) is recommended.
How far can an EV go after a 30-minute charge?
The distance an EV can travel after a 30-minute charge depends on the charger type and the EV's charging capability. With split-type DC charging (360+ kW or more), most EVs can increase their driving range by 200 to 300 km or even more while level 2 AC chargers (7-11 kW or more) add around 30 km or more.
* The data is based on theoretical values obtained by Huawei internal labs through tests carried out under specific conditions. Actual performance may vary due to differences in software versions, usage conditions, and environmental factors. All data is subject to actual usage.
* The dispenser noise is less than 50 dB(A)@25°C at 1 m. The data is based on theoretical values obtained by Huawei internal labs through tests carried out under specific conditions. Actual performance may vary due to differences in software versions, usage conditions, and environmental factors. All data is subject to actual usage.