
 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa


 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa

In an era where even a momentary power disturbance can cost millions in downtime, understanding what device for network power outages UPS is vital for any data center operator. A uninterruptible power supply(UPS) bridges the gap between mains failure and auxiliary solutions, ensuring that critical servers and networking equipment remain online and that graceful shutdown procedures can be executed. This article will explore why uninterruptible power supply(UPS)units are indispensable for data center resilience, explain their core operating principles, outline key selection criteria and examine topology choices for various grid conditions to guide your uninterruptible power supply(UPS)deployment decisions.

Data centers require continuous uptime to serve global applications, from cloud computing to real‑time financial trading. A uninterruptible power supply(UPS) acts as the first line of defense against six main power anomalies—blackouts, brownouts, sags, surges, spikes, and electrical noise—safeguarding sensitive electronics and preventing data corruption or hardware damage.
Moreover, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) supports 0ms switching across all modes: when mains power is interrupted, the uninterruptible power supply (UPS) immediately switches to battery mode, supplying direct battery power until utility power is restored or a diesel generator takes over, ensuring continuous and stable equipment operation.
● Three‑Stage Conversion Flow: Incoming AC is converted to DC by the rectifier, then the inverter converts that DC back into AC.
● Seamless Transfer on Outage: Upon failure, instantaneously shifts to battery mode in 0ms, drawing power directly from the battery and converting it via the inverter into AC for downstream equipment—ensuring uninterrupted output.
● Integrated Battery Reserve: The battery bank stores DC energy during normal operation; when utility power sags or drops out, it supplies the inverter directly until mains are restored or backup generators come online.
● Built‑In Power Conditioning: Beyond mere backup, modern uninterruptible power supply(UPS) designs employ double‑conversion topology to filter spikes, surges, and harmonics—delivering a stable sine‑wave output that protects sensitive electronics from voltage anomalies.
Selecting an optimal uninterruptible power supply (UPS) involves balancing performance, cost, and long‑term maintainability. Three pivotal factors guide this decision:
A uninterruptible power supply(UPS)should be right‑sized to your maximum expected load plus overhead for future expansion. Oversizing reduces system efficiency and increases capital cost; undersizing risks overload and battery depletion during extended outages. Typically, data centers apply an “N+1” redundancy architecture— deploying N uninterruptible power supply (UPS) units to handle the full load plus one additional uninterruptible power supply (UPS)—so that even if one uninterruptible power supply (UPS) goes offline, the remaining N units can continue to support the load without interruption.
Ease of maintenance directly impacts mean time to repair (MTTR) and overall availability. Look for models offering hot‑swappable batteries and power modules, and remote detecting capabilities. Preventive maintenance technologies, firmware update support, and manufacturer training further reduce the risk of unplanned downtime.
With uninterruptible power supply(UPS)units increasingly network‑connected for remote management, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Ensure your uninterruptible power supply(UPS)platform supports multi‑factor authentication, encrypted communications, and role‑based access control. Huawei Smart Power Supply solutions, for example, enhance operational security through its iPower function, which delivers full-chain visibility, management, and control over the entire power supply, enabling administrators to swiftly detect and investigate anomalous activities.
The resilience of your local grid influences uninterruptible power supply(UPS)topology selection:
Zero‑Transfer‑Time Assurance: In a stable grid environment, incoming AC is first converted to DC by the rectifier and then inverted back to clean AC to power equipment; only when the utility supply falters does the uninterruptible power supply (UPS) switch—within 0ms—to battery mode to maintain uninterrupted operation.
Continuous Power Conditioning: These units continuously regenerate a pure sine‑wave output, filtering out any residual noise or harmonics from the utility line for consistently clean voltage.
Tight Voltage Regulation: With regulation tolerances as low as ±1%, double‑conversion uninterruptible power supply(UPS)designs maintain precise output under varying loads, protecting high‑value servers and networking gear.
Voltage Regulation via AVR: In a line-interactive uninterruptible power supply (UPS), normal utility power is routed through an AVR transformer to the load—though this incurs some energy loss—while any grid anomaly trips the AVR offline and switches to battery power via a bidirectional converter, ensuring seamless protection.
Cost‑Efficiency: Online uninterruptible power supply (UPS) units typically deliver higher overall efficiency than line-interactive models—despite their higher upfront cost—making them the preferred choice for critical applications in regions with variable voltage.
Isolation Transformers and Active Filters: Uninterruptible power supply(UPS) solutions for extreme conditions integrate isolation transformers to block high‑energy spikes and active filters to remove electromagnetic interference, ensuring a stable supply despite severe grid anomalies.
AI Predictive Maintenance: By continuously monitoring busbar temperatures in real time via over 150 NTC sensors, Huawei Smart Power Supply transforms passive fault response into proactive prediction, identifying anomalies before they escalate into failures.
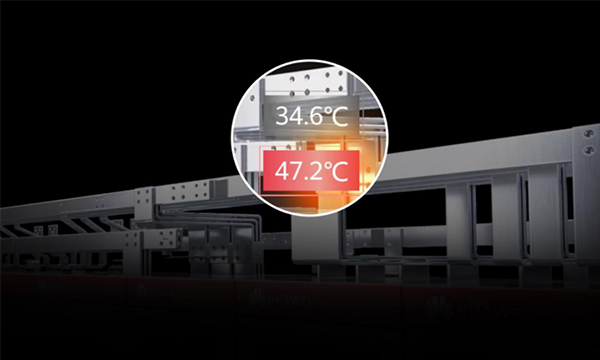
Adaptive Fault Response: By combining traditional surge protection with AI‑based diagnostics, these advanced uninterruptible power supply(UPS)not only react to disturbances but also proactively maintain battery health and system resilience.
Selecting what device for network power outages UPS is a strategic decision encompassing instantaneous backup, power conditioning, and intelligent health management. By understanding uninterruptible power supply(UPS)operation, matching capacity to load, ensuring maintainability, and enforcing cybersecurity, data centers can sustain uninterrupted service in any grid scenario. Integrating advanced solutions—such as Huawei AI‑driven Smart Power Supply solution—future‑proofs operations without overt branding, keeping infrastructures both resilient and efficient.
Critical IT equipment—servers, network switches, storage arrays—should be prioritized to ensure data integrity and service continuity. Non‑essential systems like lighting or HVAC can remain on standby to conserve uninterruptible power supply(UPS)battery capacity.
Yes. uninterruptible power supply(UPS)systems often feature multiple output circuits and rack‑mount or modular designs to distribute power across several devices. However, ensure total connected load does not exceed the UPS’s rated capacity—and maintain proper load balancing across phases in three‑phase systems.
Battery backup duration is determined by the standalone battery system—rather than the uninterruptible power supply (UPS) itself—and varies with battery chemistry and capacity. In data centers, lithium-ion batteries typically support uninterruptible power supply (UPS) output for around 15 minutes, ensuring continuous power until mains supply returns or a diesel generator takes over.