
 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa


 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa

Lithium-ion batteries are core members of the modern energy field and are continuously transforming our lives. Whether it is powering electric vehicles for long-distance travel or supplying power to data centers and being crucial for industrial power supply, all rely on its efficient functions of electrical energy storage and release. To truly understand this type of battery, we first need to lift the veil of mystery from it. Below, we will provide a detailed interpretation of how are lithium ion batteries manufactured, and also explain how are lithium-ion batteries produced.
How Lithium-Ion Batteries Work?
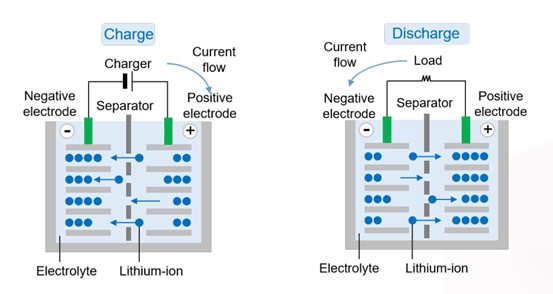
The charging and discharging of lithium-ion batteries is a process of mutual conversion between electrical energy and chemical energy.
● Charging
when an external power source applies a voltage, lithium ions and electrons in the cathodematerial are released from the transition metal in the cathode material and flow to the negative electrode through an external circuit. At the same time, positively charged lithium ions enter the electrolyte and move toward the negative electrode. The lithium ions gain electrons on the surface of the negative electrode and intercalate between layers of the anode material (usually graphite).When the lithium ions de-intercalated from the positive electrode are fully intercalated into the negative electrode, the battery is fully charged and the negative electrode is in a lithium-rich state.
● Discharging
when the battery is connected to an external load, it begins to discharge. Because there is apotential difference between the positive and negative electrodes, lithium ions de-intercalate from the negative electrode, pass through the electrolyte and the separator, and return to the positive electrode to recombine with the cathode material. Meanwhile, the electrons at the negative electrode also flow through an external circuit to the positive electrode to form a current and provide electric energy for the load.
Raw Materials and Core Components
● Raw Materials
Lithium: A key element in lithium-ion batteries, mainly used in electrolytes and other components.
Cobalt: Enhances battery stability and energy density.
Nickel: Helps improve energy density, allowing the battery to store more energy.
Manganese: Contributes to the stability and safety of the battery, often used in combination with nickel and cobalt.
Graphite: A commonly used anode material, known for its high electronic conductivity and other advantages.
● Core Components
Positive electrode: Common materials include lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganate oxide, ternary materials, and lithium iron phosphate, each with unique characteristics in terms of energy density, safety, and other factors.
Negative electrode: Mainly made of graphite, along with other materials such as hard carbon, soft carbon, lithium titanate, Si-based, and Sn-based materials. Each material varies in terms of specific capacity, cycle life, and other properties.
Electrolyte: Composed of lithium salts (such as lithium hexafluorophosphate) and organic solvents (such as ethylene carbonate and dimethyl carbonate), the electrolyte provides the medium for lithium-ion migration.
Separator: Typically made from polyethylene, polypropylene or composite membranes, the separator serves to electrically insulate and provide a channel for lithium-ion migration.
● Step-by-step Process
The production of lithium-ion batteries involves the following key steps:
1. Raw material preparation: Prepare raw materials such as positive and negative electrode materials, electrolytes, separators, current collectors, etc., and inspect their quality.
2. Electrode plate production: Mix the active materials for the positive and negative electrodes with conductive agents, binders, and other additives to form a slurry. This slurry is coated onto aluminum foil (for the positive electrode) and copper foil (for the negative electrode), followed by drying, rolling, and cutting to form the electrode sheets.
3. Separator treatment: Select appropriate separator materials, cut them to the required size, and dry them.
4. Cell assembly: Assemble the positive and negative electrode sheets and the separator into a cell by means of winding or lamination, and lead out the positive and negative electrodes.
5. Electrolyte injection and sealing: Inject a precise amount of electrolyte into the battery cell under vacuum, then seal the cell.
6. Formation: Carry out the first charge and discharge to form a SEI film, activate the performance, and then conduct an aging treatment.
7. Testing and sorting: Perform comprehensive testing of the battery’s performance, and sort them according to their performance.
8. Packaging and shipping: Package the batteries according to requirements, and deliver them to customers after inspection.
Through the above content, we have comprehensively understood how lithium ion batteries are manufactured, the raw materials used in their production, and the complex and rigorous manufacturing processes. Among the many li ion battery manufacturers, Huawei SmartLi stands out for its superior performance and safety. From the raw materials to the completion of the cell production line, there are more than 300 controls over dust and foreign objects. There are also double-layer multi-module ovens that preheat, rapidly evaporate, and cool the electrode sheets in segmented baking. The negative electrode sheets adopt the advanced double-roll process, ensuring better consistency and safety of the cells. Every detail, from raw materials to the finished product, is meticulously controlled, ensuring that users of SmartLi enjoy lasting and efficient power support.

How are lithium-ion batteries made step by step?
The manufacture of lithium-ion batteries is mainly divided into eight steps: raw material preparation, electrode plate production, separator treatment, cell assembly, electrolyte injection and sealing, formation, testing and sorting, and packaging and shipping.
What are the raw materials for lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are mainly composed of four major raw materials, which are: positive electrode, negative electrode, electrolyte, and separator.
How difficult is it to manufacture lithium-ion batteries?
The manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries is quite challenging, primarily due to the following factors: material development must balance performance with various application requirements; the production process is complex, with high precision and stability requirements at each stage; there are many quality inspection tasks that ensure cell consistency; and multiple safety measures must be implemented to prevent risks such as thermal runaway.
What are the key processes in manufacturing lithium-ion batteries and what precautions should be taken?
The key processes in manufacturing lithium-ion batteries mainly include material preparation, electrode manufacturing, battery assembly, electrolyte injection, encapsulation, and testing. Strict quality control ensures battery performance and safety.