
 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa


 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa

Lithium-ion batteries are the "star players" among energy storage batteries. They can be found everywhere, from smartphones and tablets to electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage networks. If you want to have an in-depth understanding of "what is li-ion battery", this popular science article will satisfy your curiosity. Questions that people generally care about, ranging from the working principle and type classification to the advantages, application scenarios, and safe use of lithium-ion batteries, will all be answered.
What is li-ion battery? In terms of the working principle, this type of battery can complete charging and discharging by allowing lithium ions to intercalate into and deintercalate from the positive and negative electrodes alternately, thus achieving efficient conversion between electrical energy and chemical energy.
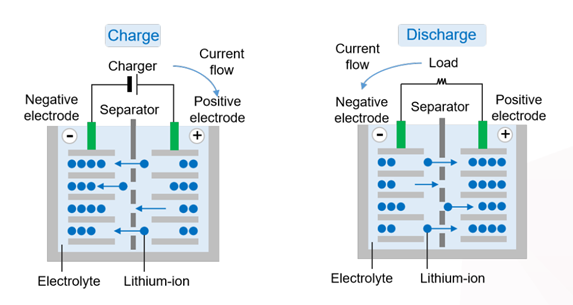
After introducing "what is li-ion battery", let's take stock of its classification. According to the positive electrode materials, there are mainly the following types:
Lithium-ion batteries are also used in fields such as the Internet of Things, smart homes, medical devices, aerospace, etc. For instance, smart lighting systems installed at home and medical devices like portable ventilators.

The safety risks of lithium-ion batteries stem from multiple aspects. Design flaws of the batteries, mismatch of the cell materials, and lax quality control during production can all potentially become sources of danger. Improper use or abuse of the batteries can also lead to safety issues such as insulation failure, swelling, valve opening, and thermal runaway.
In response to this, we not only need to understand "what is li-ion battery" and ensure safety from the source of the products, but also strengthen the awareness of prevention and control and establish a strict and standardized safety protection system.
For example, when supplying power to medium and large-sized data centers, lithium-ion batteries using lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells, known for their superior thermal stability, should be the preferred choice. Take Huawei SmartLi (lithium-ion battery) as an example, It carefully selects lithium iron phosphate cells with high consistency, which have high stability. It is also equipped with a PACK-level fire extinguishing device, which can accurately suppress the thermal runaway of a single cell under high-temperature tests.
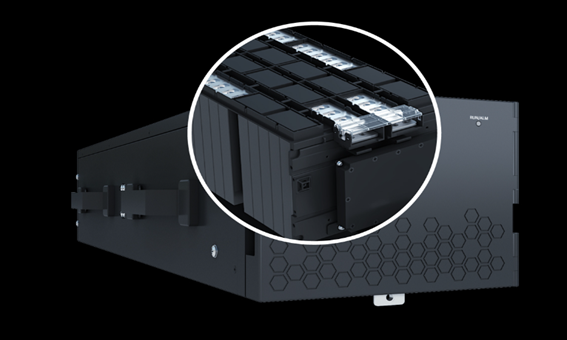
At the same time, Huawei SmartLi adopts a 3D cellular protection net and an all-plastic compartment design to isolate micro-short circuits. With AI predictive maintenance, enabling real-time leakage current detection, precise fault identification, and millisecond-level risk elimination. It can also actively isolate risks such as over-temperature, over-voltage, over-current, and under-voltage through a multi-level BMS protection system.
In the construction of the safety protection system, in addition to regularly and comprehensively conducting risk inspections of lithium-ion batteries in a standardized manner, we should also focus on aspects such as automatic fire extinguishing systems, ventilation, smoke prevention and exhaust, and thermal runaway detection and alarm. We should arrange fire-fighting facilities in a targeted manner and prepare in advance emergency plans for situations such as fires and explosions.
What is li-ion battery ? This new - type energy - storage battery with multiple advantages has already been deeply integrated into all aspects of production and daily life. Nevertheless, to use lithium - ion batteries safely and efficiently, we still need to choose reliable products and take sufficient safety precautions.
Lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries are not the same thing. The positive electrode material of a lithium battery is manganese dioxide or thionyl chloride, and the negative electrode is metallic lithium. It is a disposable battery, and it cannot be recharged after the power is used up. For a lithium-ion battery, a lithium-containing compound is used as the positive electrode, and it can be charged and discharged repeatedly.
When it comes to "lead-acid battery vs lithium-ion battery", the latter has quite a few advantages. With a high energy density, lithium-ion batteries can meet the power supply requirements with a smaller volume and weight. Their excellent charge-discharge cycle ability gives them a long lifespan, making them more durable and resulting in lower long-term usage costs. They do not contain heavy metals like lead, so they are environmentally friendly.
Lithium-ion battery is a secondary battery that uses a lithium-containing compound as the positive electrode. It can achieve repeated charging and discharging through the reciprocating movement of lithium ions between the positive electrode and the negative electrode. This type of battery has the advantages of high energy density, light weight, fast charging, long lifespan, etc., and has a very broad application prospect.
The service life of lithium-ion batteries is generally longer than that of traditional batteries, but it is not fixed. Different types of lithium-ion batteries have different cycle lives. Among them, lithium-ion batteries are known for their "longevity". Their cycle life can even reach more than 10,000 times, and they can easily be used for 10 years. If lithium-ion batteries can be used and maintained reasonably, their actual service life is expected to be further extended.