
 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa


 Search
Search


Asia Pacific
Europe
Latin America
Middle East & Africa

In the era of rapid digitalization, lithium‑ion batteries serve as the core electrochemical energy storage devices, found in nearly every field and playing a critical role in ensuring continuous and reliable power—especially in data centers. However, as their applications expand, so do the questions: How do lithium-ion batteries actually work? are lithium ion batteries safe? are lithium ion batteries safe for the environment? And how can you ensure their safety and perform daily maintenance? This article dives deep into these issues to fully demystify lithium‑ion batteries.
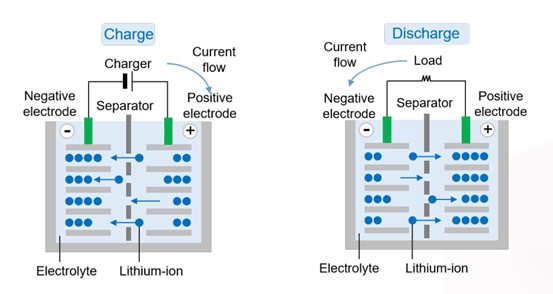
The working principle of lithium ions mainly relies on the reciprocal movement of lithium ions between the positive electrode and the negative electrode.
The following is a detailed explanation:
● Charging process:The voltage generated by an external power source prompts lithium ions and electrons in the cathode material to be released from the transition metal. The electrons flow to the anode through the external circuit, while the lithium ions enter the electrolyte, pass through the separator membrane, reach the anode, and are embedded between the layers of the anode material (usually graphite). When the anode is fully embedded with lithium ions, the battery is fully charged, and at this time, the anode is in a lithium-rich state.
● Discharging process: When the battery is connected to an external load, the discharging operation begins. Due to the potential difference between the positive and anodes, it can drive the lithium ions to de-intercalate from the anode, pass through the electrolyte and the separator membrane again, and return to the cathode to recombine with the cathode material. At the same time, the electrons at the anode flow to the cathode through the external circuit, thus forming an electric current to supply power to the load.
How safe are Lithium-Ion batteries? The safety of lithium-ion batteries is a complex issue influenced by multiple factors.
we can look at it from three aspects:
At the battery cell level, common failure modes include:insulation failure, abnormal swelling, valve opening, and thermal runaway, etc.
● Insulation failure
This is usually caused by excessively high internal pressure in the battery, leading to the oxidation and decomposition of the electrolyte to generate gas.
● Abnormal swelling
This typically occurs under abusive operating conditions when the electrolyte generates a large amount of gas, causing the internal pressure to exceed the threshold of the battery safety valve.
● Valve opening
The inducing factors mainly include mechanical damage, overcharging, internal short circuits, etc. Under the influence of these factors, the active materials inside the lithium-ion battery undergo intense exothermic reactions. When the internal temperature of the battery exceeds the controllable range, it ultimately leads to thermal runaway.
Lithium-ion batteries using lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells offer high reliability and long lifespan, making them the preferred backup power solution for data centers.
For example, Huawei SmartLi strictly selects high-consistency LFP cells, which will not catch fire even if pierced. It employs a 3D cellular protection net and all-plastic compartment, providing reliable insulation and effectively isolating micro-short circuits.
It is also equipped with pack-level fire extinguisher that can precisely suppress thermal runaway of cell, alongside smart fault prediction features that offer real-time leakage detection and millisecond-level fault identification to eliminate hidden risks.
In addition, it is equipped with multi-level BMS protection, which can actively isolate risks such as overtemperature, overvoltage, overcurrent, and undervoltage, making the lithium battery safer and greatly reducing usage risks.

Lithium-ion batteries for data centers shall be deployed based on comprehensive factors including cost-effectiveness and safety.
Remote skid-mounted deployment with an independent container or cabinet is preferred. Remote deployment in an independent structure or building is an alternative. If the remote deployment conditions are not met, batteries can be deployed in an independent room against the exterior wall of the building where the main equipment room is located.
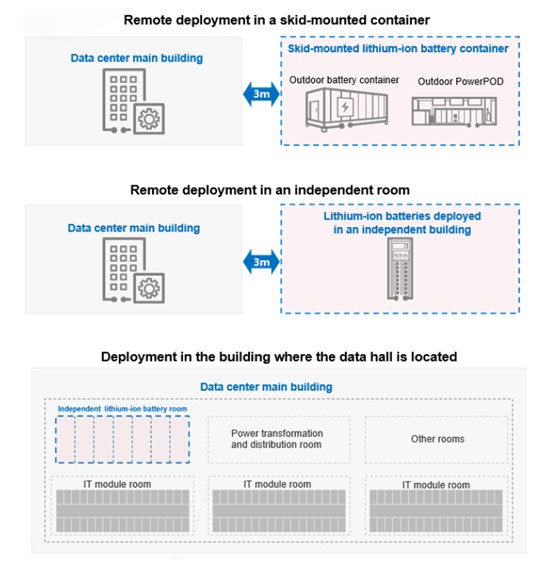
In the remote deployment scenario, the fire safety distance of the lithium-ion battery room must be properly determined based on the height of the lithium-ion battery room or the height of the building in which the lithium-ion battery room is located, the fire resistance rating, and the fire hazard.
The recommended fire safety distance and fire resistance rating are as follows:
● If the fire resistance limit of a remotely deployed skid-mounted container, structure, or building is not less than 1 hour, the fire safety distance between the container, structure, or building and other buildings shall be not less than 3 m.
● If the fire resistance limit of the wall of a remotely deployed skid-mounted container, structure, or building opposite to other buildings is greater than or equal to 2 hours, and the fire resistance limit of the other sides is greater than or equal to 1 hour, the fire safety distance between the container, structure, or building and other buildings must be greater than or equal to 1 m.
When the lithium-ion battery room is deployed in the building where the data hall is located, the capacity of a single lithium-ion battery room shall not exceed 600 kWh. The lithium-ion batteries shall be deployed in a room against an exterior wall.
In addition, the room shall also comply with the following requirements:
● The fire resistance limit of beams, columns, walls, and sealed holes in the room shall not be less than 2 h;
● The top and bottom floors shall not be less than 1.5 h;
● The evacuation door shall be a fire door that can withstand fire for at least 1.5 h;
● Protective measures, such as a vestibule, shall be provided at the junctions between stairways, outdoor stairways, or hazardous areas and adjacent areas.
● The wall of the vestibule shall be a fire wall with a fire resistance of at least 2 h;
● The door shall be a fire door with a fire resistance of at least 1.5 h and shall not be installed in line with the staircase door
Lithium-ion batteries have unique fire characteristics, including :
● High temperature rise rate and Heat Release Rate
● Fast Fire Spread
● Complex Fire Extinguishing and Easy Reignition
● Generation of Combustible and Toxic Gases
Therefore, extinguishing lithium-ion battery fires requires two aspects:
● Rapidly extinguish the open flame of the battery;
● Use fire extinguishing agents with cooling and heat dissipation functions to prevent the battery from reigniting.
Both domestic and international full-scale fire tests and relevant standards recognize water as the preferred fire extinguishing agent for suppressing lithium-ion battery fires. With extremely high heat capacity and latent heat of vaporization, water absorbs a large amount of heat through phase changes in a fire scene. After vaporizing into water vapor, its volume expansion can reduce oxygen concentration. Water not only has excellent fire-extinguishing and cooling performance but is also low in cost and easy to use.
Therefore, water is the first choice for suppressing lithium-ion battery fires, and fire extinguishing systems using water as the extinguishing agent should be adopted in lithium-ion battery rooms of data centers.
Common water-based fire extinguishing systems include automatic water spray extinguishing systems, automatic sprinkler systems, and fine mist fire extinguishing systems.
For data centers, automatic water spray extinguishing systems are prioritized, followed by automatic sprinkler systems and then fine mist fire extinguishing systems. Meanwhile, fire water supply systems and fire extinguishers should be installed in lithium-ion battery rooms of data centers to ensure effective fire suppression.
The environmental safety of lithium-ion batteries is a growing concern. In fact, as long as effective measures are taken in the production, use, and recycling processes—such as using environmentally friendly materials, strengthening safety monitoring during use, and establishing a sound recycling system to effectively recycle and reuse lithium-ion batteries—the negative impact of lithium-ion batteries on the environment can be reduced, thereby achieving the goals of environmental friendliness and circular resource utilization.
Lithium-ion batteries, relying on their unique working principles, are widely applied in fields such as data centers. So, are lithium ion batteries safe? From the detailed analysis of lithium-ion batteries above, it is clear that while lithium-ion batteries do pose certain safety risks and environmental impacts, choosing products like Huawei SmartLi, which offers multiple safety guarantees and real-time safety monitoring from materials to technology, can significantly reduce these risks. Moreover, with continuous technological innovation, the safety and environmental friendliness of lithium batteries will continue to improve.
Lithium-ion batteries should be stored indoors, protected from direct sunlight and rain. The storage area must be dry, well-ventilated, and maintained within proper temperature and humidity ranges.
Routine inspections of lithium-ion batteries are mainly divided into: daily inspections, monthly inspections, quarterly inspections, and annual inspections. These inspections primarily involve comprehensive checks and maintenance of the working environment, product components, fire protection systems, etc., of lithium-ion batteries to ensure their safe and stable operation and extend their service life.
The safety of lithium-ion batteries varies by type. For example, Huawei Smart Lithium Battery utilize lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells, which provide good thermal stability and a low risk of thermal runaway, offering safety advantages over some other battery types.
Different environmental conditions have a significant impact on the performance of lithium-ion batteries in data centers.
In terms of temperature, high temperatures accelerate the internal reactions of the battery, which may trigger thermal runaway, while low temperatures reduce the charging and discharging performance and capacity.
In terms of humidity, excessively high humidity can easily corrode the battery and increase the risk of short circuits, and excessively low humidity will cause the electrolyte to dry up, affecting ion conduction.
In addition, dust may block the heat dissipation channels, and corrosive gases will corrode the battery electrodes and the casing. All these are detrimental to the battery's performance and safety.