How to Charge EV at Home and Public Stations: Step-by-Step
How to Charge EV? Home, Work & Public Charging Explained
When you have got an electric vehicle (EV) or you are thinking about getting one—awesome choice! But now comes the big question: how do you charge an EV? Unlike gas cars, which you refuel by pulling up to a pump, EVs have different charging options. You can plug in at home, top up at work, or use a public charging station.
Understanding the ins and outs of how to charge EV—where to do it, how long it takes, and how much it costs—will help you stay powered up with ease. Let's break it all down so you can charge your EV efficiently and affordably!

How to Charge an EV?
Charging an EV is straightforward once you know your options. The main methods are charging at home, at your workplace, or at public charging stations. Each has its own advantages and things to consider. Let's break down what you need to know for each scenario:
At Home
Charging at home is the most convenient option for many EV owners: you simply plug in your car when you are home, and it charges while you relax. There are two home charging methods:
Level 1 (Basic Home AC Charging)
This means plugging your EV into a household outlet (the same type you use for a phone charger or kettle) with the charger it comes with. It is the slowest way to charge, adding about 10 km of range per hour. Level 1 is relatively simple and convenient if you have plenty of time overnight or your daily driving is light.
Level 2 (Fast AC Charging)
This uses a dedicated home EV charger unit (often called a wall box), but at higher power (usually 7 kW to 11 kW or even more, such as three-phase power). A Level 2 charger can charge your EV much faster, typically adding about 50 km or even more of range per hour.
To install a Level 2 home charger, you will need a qualified electrician. If your home only has single-phase electricity (common in many houses), a 7 kW charger is suitable. Houses with three-phase power can support chargers up to 11 kW or even more (faster charging).

At Workplace
Charging at your workplace is another convenient option, especially if your employer or office building provides EV charging stations. Many companies are beginning to install chargers in their parking areas as a perk for employees and a step toward sustainability.
Workplace chargers are usually Level 2 AC chargers (7 kW to 11 kW or more) that can add about 50 km or more of range per hour. Since your car will be parked for several hours during the workday, you can gain a substantial amount of charge while you work, often a full recharge if you plug in for the whole day.
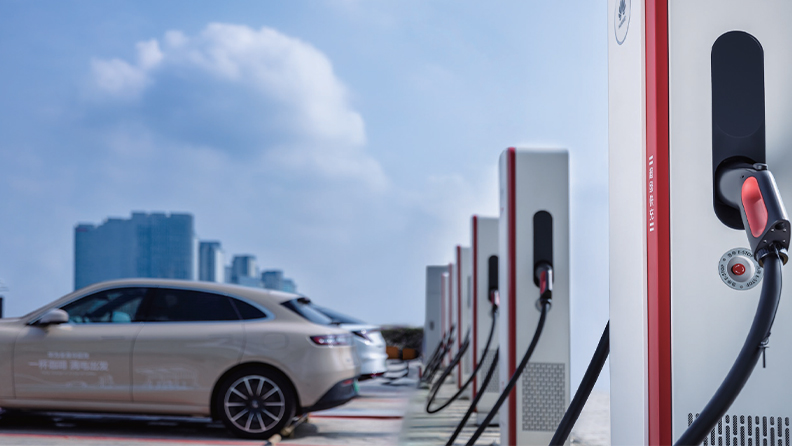
At Public Stations
Public EV charging stations are located in many areas, such as shopping mall parking lots, highway rest stops, petrol stations, and dedicated charging hubs. They are crucial for charging on the go or during road trips.
Public chargers come in two main types:
Level 2 Fast AC Chargers
These are similar to home/work chargers and often have power levels from about 7 kW to 11 kW or more. AC public stations are common in malls, hotels, or public parking garages. Charging time here is moderate: you might gain about 50 km or ever more of range per hour on a 7 kW AC charger.
Level 3 integrated DC Chargers
These are the high-speed charging stations found at highway rest stops, petrol stations, and major city hubs that can rapidly charge your EV's battery. Unlike Level 1 and 2 AC chargers that rely on your car's On-Board Charger (abbreviated as OBC), DC fast chargers feed high-power direct current (DC) to the battery.
Power levels for DC chargers can range from about 40 kW up to 300 kW or more. A 50 kW DC charger can charge an EV to around 80% in roughly 1 hour, while newer chargers with a power of 150 to 180 kW or even higher take less time to achieve the same charging effect. This makes long-distance travel much easier: you can take a short break and be back on the road with plenty of range.
New Level integrated DC Chargers
Huawei Digital Power's Liquid-Cooled Ultra-Fast Charging solution can deliver up to 500 A charging current, enabling ultra-fast charging speeds. You can gain 200+ km* of range in just 5 minutes, making it one of the fastest charging solutions available.
Plus, it operates at noise levels below 50 dB*, ensuring a quieter charging experience while maximizing efficiency at 95.5%. This system is designed for long-term reliability, with a low annual failure rate of under 0.5%*, ensuring consistent performance over a decade of operation.

Where to find a public charger?
Locating a public charging station is getting easier with smartphone apps and maps. You can use apps on your cellphone to find nearby stations, check their availability, and even pay for the session.
How Long Does It Take to Charge an EV?
Now that you know how to charge EV at home, work, or on the go, the next question is “How long will it take to charge my car?” The answer is: it depends on the type of charger and your car's battery capacity.
Level 1 (Slow Home AC Charging)
Using a basic home outlet (around 2 to 3 kW output) is the slowest method. It usually adds about 10 km of range per hour of charging. For a full charge:
A small 40 kWh battery might take roughly 12–18 hours to charge fully.
A mid-size 60 kWh battery could need around 18–25 hours for a full charge.
An 80 kWh battery could take 25-30+ hours (nearly two days if charging from 0%)
In real life, if you do not have a long daily travel distance, you can consider charging your electric vehicle at home in the evening. Level 1 charging will be more suitable if your electric vehicle has a small battery capacity or when no faster charger is available.
Level 2 (Faster Home/Work AC Charging)
This is the most common method for regular charging because it balances speed and convenience. Level 2 chargers can add 50 km or more of range per hour at 7 kW. Typical full charge time:
40 kWh battery: ~6-7 hours for 0–100% (easily done overnight or during a work shift).
60 kWh battery: ~8-10 hours for full charge.
80 kWh battery: ~10-12 hours for full charge (might stretch just past overnight, but if you charge every night, you likely never hit empty anyway).
If you have access to an 11 kW or more charger (some condos or workplaces with three-phase power), the time drops further. In practice, this means you can recover a lot of range in just a few hours.
DC Fast Charging
DC fast chargers are the quickest way to charge an EV. They can have high DC output of 50–360 kW or even up to 480 kW and charge your car up very quickly. The exact time depends on the charger's power and your car's capability:
50 kW DC charger: Common in many public stations, it can typically charge an EV from 0% to 80% in about 60-90 minutes.
360 kW DC charger: In ideal conditions, charging from 10% to 80% takes just 30 minutes. However, it is important to note that if the battery level is too low or too high, the charging speed will slow down. For example, charging from 1% to 100% is estimated to take around one hour.
480kW (or higher) DC charger: As a high-performance charging device, a 480 kW DC charger can replenish a large amount of electrical energy for a vehicle in a shorter time, and its charging efficiency can usually reach over 90%. Taking an electric vehicle with a range of 500 km as an example, when using a 480 kW DC charger, the charging time may only take dozens of minutes or even less. This is very practical for users who are in urgent need of a quick charge.
Conclusion
Learning how to charge EV is a new experience, but a rewarding one. You have the flexibility to charge at home while you sleep, at work while you focus on your job, or at numerous public stations when you are out and about. It takes a bit longer than pumping petrol, but with a little planning – like overnight home charging or a coffee break during a fast charge – it fits comfortably into your routine. Plus, you will enjoy much lower fuel costs and the satisfaction of driving a car that is cleaner for the environment.
As the world moves toward carbon neutrality, Huawei Digital Power is leading the way with clean energy and smart eMobility solutions to make EV charging more efficient and sustainable. Our FusionCharge Liquid-Cooled Ultra-Fast Charging Solution can provide a charging current of up to 500 amperes without excessive heat buildup, replenishing your electric vehicle with a driving range of over 200 km in just five minutes. Meanwhile, the FusionCharge DC Charging Power Unit optimizes energy use with intelligent peak shaving and seamless integration with future solar and energy storage systems. With these cutting-edge innovations, EV infrastructure is getting faster, smarter, and greener.
FAQs
How can I charge my EV car?
You can charge your EV at home using a standard outlet or install a dedicated Level 2 faster wall-box charger, at work if your office provides EV stations, or at public chargers, which include Level 2 AC chargers in malls and DC fast chargers at highways for quick top-ups.
Can I plug an EV into a regular outlet?
Yes, you can plug an electric car into an ordinary household power outlet. This method is called level 1 charging. However, its charging speed is very slow, usually increasing the mileage by about 10 km per hour, depending on the size of the battery.
How do you charge an EV at a public charging station?
To charge an EV at a public station, find a charger that is compatible with your EV's port, then plug in. Start the session via RFID, app, or credit card, and monitor charging. Once done, stop charging, pay if required, unplug, and move your car.
* The data is based on theoretical values obtained by Huawei internal labs through tests carried out under specific conditions. Actual performance may vary due to differences between software versions, usage conditions, and environmental factors. All data is subject to actual usage.
* The dispenser noise is less than 50 dB(A)@25°C at 1 m. The data is based on theoretical values obtained by Huawei internal labs through tests carried out under specific conditions. Actual performance may vary due to differences between software versions, usage conditions, and environmental factors. All data is subject to actual usage.


 Search
Search
 EN
EN